LIVE | What Economic Survey says on GDP, inflation, and more
The growth estimated by the Economic Survey, ahead of the Union Budget, is in line with the International Monetary Fund’s estimate of 7 per cent

Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman tabled the Economic Survey 2023-24 in Parliament on Monday (July 22), ahead of the Union Budget on Tuesday. The Survey is authored by Chief Economic Advisor V Anantha Nageswaran and his team.
Following are the highlights of the document:
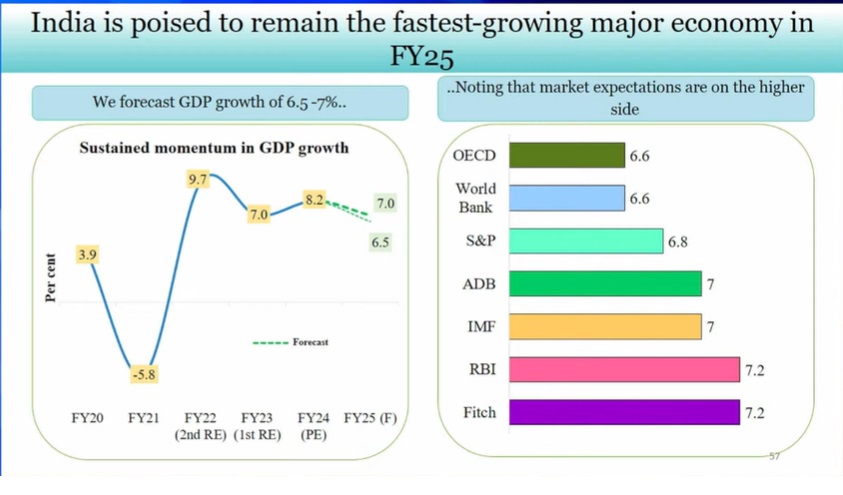
- Economic growth projected at 6.5-7% in FY25 versus 8.2% in 2023-24
- Unprecedented third popular mandate of Modi government signals political, policy continuity
- Domestic growth drivers supported economic growth in FY24 despite uncertain global economic performance
- Indian economy on a strong wicket and stable footing, demonstrating resilience in the face of geopolitical challenges
- To sustain post-pandemic recovery, there has to be heavy lifting on the domestic front
- Reaching agreements on key global issues like trade, investment and climate, has become extraordinarily difficult
- Short-term inflation outlook benign, but India faces persistent deficit in pulses and consequent price pressures
- Expectations of normal monsoon, and moderating global prices of imports give credence to benign inflation projections by RBI
- Hardships caused by higher food prices for poor and low-income consumers can be handled through direct benefit transfers or coupons for specified purchases valid for appropriate durations
- Ways suggested to explore whether India’s inflation targeting framework should target the inflation rate excluding food items
- Escalation in geopolitical conflicts and its impact may influence RBI’s monetary policy stance
- Outlook for India’s financial sector appears bright
- As financial sector undergoes critical transformation, it must brace for likely vulnerabilities originating globally or locally
- Healthier corporate and bank balance sheets will further strengthen private investment
- India’s policy adeptly steered through challenges, ensuring price stability despite global uncertainties
- Tax compliance gains, expenditure restraint, and digitisation help India achieve fine balance in govt's fiscal management
- Capital markets becoming prominent in India's growth story; market resilient to global geopolitical, economic shocks
- AI casts a huge pall of uncertainty over the impact on workers across all skill levels
- Increased FDI inflows from China can help India enhance participation in global supply chain, boost exports
- As much as 54 pc of disease burden due to unhealthy diets; need transition towards balanced, diverse diet
- Remittances to India to grow at 3.7 pc to USD 124 billion in 2024, 4 pc in 2025 to reach USD 129 billion.
The Economic Survey is an annual document presented by the government ahead of the Union Budget to review the state of the economy.
The document also provides an overview of the short-to-medium-term prospects of the economy.
The Economic Survey is prepared by the Economic Division of the Department of Economic Affairs in the Ministry of Finance under the supervision of the chief economic adviser.
(Follow our Live updates below)
Live Updates
- 22 July 2024 4:00 PM IST
Strategic reforms needed to build care economy
Strategic reforms are required to build a solid care economy structure in India, as the country faces the challenge of “motherhood penalty” with a drop in female labour force participation rate around childbearing years, the Economic Survey 2023-24 said on Monday.
The survey estimated that direct public investment equivalent to 2 per cent of the GDP has the potential to generate 11 million jobs in the sector, nearly 70 per cent of which will go to women.
Subsidising care services can be considered, said the survey, asserting that the successful international models of Australia, Argentina, Brazil, and the US in this sector may offer valuable insights for India. These countries provide financial assistance through vouchers and tax rebates to the care workers based on their income, child's age, number of offspring, etc.
“The economic value of developing a care sector is twofold - increasing female labour force participation rate (FLFPR) and promoting a promising sector for output and job creation. According to International Labour Organisation (2018), the care sector is one of the fastest-growing sectors globally, and investments in the care services sector are estimated to generate 475 million jobs globally by 2030.
“In the case of India, direct public investment equivalent to 2 per cent of GDP has the potential to generate 11 million jobs, nearly 70 per cent of which will go to women,” the survey stated.
It pointed out that a wide range of research has emphasised the impact of affordable and reliable child-care on freeing women's time for paid employment, enhancing mental health and improving children's learning and nutrition. However, it said the literature on this is mainly foreign and empirical studies on India are scarce.
According to the survey, the impact of childbearing and child-care is found to have a significant cost on women's careers. This 'motherhood penalty' is depicted as a drop in FLFPR around childbearing years and a loss of income.
Women tend to be concentrated in farming and informal jobs as a result of 'motherhood penalty' as those workspaces are compatible with their personal care responsibilities, the survey said citing a study.
Even though the time spent on unpaid care work per day is only 9 minutes higher for rural women vis-a-vis urban women, higher rural FLFPR could be explained by the flexibility, in terms of timing and proximity of employment, which allows child supervision, which rural jobs typically provide, it said quoting another study.
Asserting that strategic reforms are required to build a solid structure of the care economy, the survey recommends support for parental leave policies; subsidies for care services; public and private investments in building care infrastructure; mechanisms for skill training for care workers; and mechanisms for monitoring service quality and benchmarks.
It highlighted the need for setting up a dedicated Care Sector Skills Council to help develop a skill training framework for the care sector, formulate skilling modules, and undertake partnerships with international skill training institutes.
“Public-private partnerships (PPP) could play a significant role in building the care infrastructure, especially institutions for child-care and the elderly. Policies may be formulated to invest in mobile creches in offices, hospitals, and other public areas, encouraging women to take up paid employment opportunities,” said the survey.
- 22 July 2024 3:45 PM IST
Crop insurance to see growth from 2024 onwards
The agriculture insurance sector is likely to register growth from 2024 onwards, with an average real premium growth of 2.5 per cent over the medium term, according to the Economic Survey 2023-24.
The survey, tabled in Parliament on Monday, noted that agriculture insurance, accounting for about 12 per cent of the non-life insurance market, witnessed flat growth in FY23 due to a sharp decline in premium rates in the Kharif cropping season.
However, this decline was more than offset by increased insured land area and farmer enrolments during the season, it added.
"Agriculture premiums will likely rise from 2024 onwards, with an average real premium growth of 2.5 per cent over the medium term, supported by improvements in insurance infrastructure such as mobile applications and remote sensing for crop loss monitoring," the survey said.
To address current concerns around crop insurance, the government has launched various technological initiatives. These include the YES-Tech Manual, WINDS portal, and enrolment app AIDE/Sahayak to assess crop damage via satellite-based advanced technologies.
The survey also highlighted door-to-door enrolment initiatives aimed at making crop insurance more accessible to farmers.
These measures are expected to enhance the efficiency of crop damage assessment and improve the overall accessibility of agricultural insurance in the country.
Currently, the government is implementing Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana and the Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme. - 22 July 2024 3:43 PM IST
Balancing growth and green goals a tightrope walk for India
India's path to sustainable development is fraught with challenges, as the country grapples with the twin imperatives of meeting burgeoning energy demands and reducing carbon emissions, the Economic Survey 2023-24 revealed on Monday.
Tabled in Parliament, the Survey underscores the complexities of India's green transition, emphasizing the need for a diversified energy portfolio to achieve ambitious growth targets while adhering to climate commitments.
"Balancing development needs with a low-carbon pathway is a tightrope, especially when financed predominantly through domestic resources," the Survey noted, highlighting the financial strain of pursuing cleaner energy alternatives.
The document stressed the critical role of non-fossil fuel sources in meeting India's Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and Net Zero goals. However, it also pointed out the challenges associated with renewable energy, including intermittency issues, waste management concerns for nuclear and solar technologies, and the potential impact of biofuel production on food security.
Acknowledging the importance of energy security, the survey advocated for a multi-pronged approach. It suggested diversification of energy sources, including renewables, nuclear, and biofuels; continued reliance on thermal power, particularly coal, to provide baseload support for renewable deployment; promotion of clean coal technologies like gasification and carbon capture, and enhanced international cooperation in R&D for emerging green technologies.
The Survey cautioned against over-reliance on imports, noting that while India's dependence on petroleum imports is well-known, the shift to renewable energy could lead to new vulnerabilities in the supply chains for solar panels and critical minerals.
On a positive note, the report highlighted India's significant progress in its mission-mode approach to addressing climate change. As of May 31, 2024, the share of non-fossil sources in installed electricity generation capacity has reached 45.4 per cent, putting India on track to meet its updated NDC target of 50 per cent by 2030.
The Survey called for a "more balanced approach" to climate change, suggesting policymakers focus on "nearer-term policy goals of improving human welfare" rather than being "excessively preoccupied" with long-term global climate management.
While acknowledging India's achievements, the survey emphasized the need for financial support from developed countries.
With financing needs estimated at USD 2.5 trillion (at 2014-15 prices) for meeting NDC targets till 2030, access to finance and technology at reasonable costs is crucial to ease the resource constraints.
- 22 July 2024 3:42 PM IST
Gender budget increased consistently
From Rs 97,134 crore in Financial Year 2014, the gender budget has consistently increased, reaching Rs 3.1 lakh crore in FY 2025, the Economic Survey said on Monday.
This marks a 38.7-per cent rise compared to FY24 and a 218.8-per cent increase over FY14, now constituting 6.5 per cent of the total Union Budget. In a transformative move, India is shifting from women's development to women-led development, according to the Economic Survey presented in Parliament.
The survey underscores the government's legislative interventions and provisions to ensure women's participation in various professions.
India's G20 presidency in 2023 also highlighted "women-led development" as a priority amid increasing global attention on women's workforce participation, it said.
Addressing the various issues affecting women, the survey emphasises the need for a comprehensive and pragmatic approach.
This includes improving access to basic necessities, such as sanitation, piped water and menstrual hygiene, along with ensuring safety, proper nutrition and equal opportunities in economic and political spheres.
The government's multi-faceted initiatives to enhance women's well-being are evident in the steady rise in the gender budget, the survey said.
From Rs 97,134 crore in FY14, the gender budget has consistently increased, reaching Rs 3.1 lakh crore in FY25. This marks a 38.7-per cent rise compared to FY24 and a 218.8-per cent increase over FY14, now constituting 6.5 per cent of the total Union Budget, it added.
Social empowerment initiatives, such as "Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao", have improved the sex ratio at birth and reduced maternal mortality rates. Institutional deliveries have increased and programmes like the Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, which provides cash incentives to new mothers, have shown positive impacts on long-term public health service utilisation, it added.
The survey highlighted the importance of nutritional security for women and children through programmes like the Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0. This initiative addresses malnutrition by focusing on health, wellness and immunity through micronutrient sufficiency and promoting best practices in nutrition and health.
Access to basic necessities like toilets, clean cooking-gas connections and tap drinking water under various schemes has transformed the lives of women, particularly in rural and low-income households, the survey said.
These initiatives not only address safety and dignity concerns but also free up time for productive work, it added.
The government's efforts to ensure women's safety through one-stop centres and the "Sambal" scheme, alongside educational and skilling programmes, have also been highlighted in the survey. Gender parity in school enrolment and increased participation in skill-development programmes are paving the way for greater female participation in the labour force, the survey said.
It also pointed out the need for supportive infrastructure, such as safe transport and childcare, to fully realise the benefits of these skilling programmes. The representation of women in STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) fields and their participation in non-conventional sectors like the military and police forces have also been emphasised.
Political empowerment through the Nari Shakti Vandan Abhiniyam, 2023, which ensures greater women's representation in public offices, marks a significant step towards inclusive growth and gender equality, the survey said.
Financial inclusion efforts, including the Prime Minister Jan Dhan Yojana, have facilitated access to banking services for women, enhancing their control over household resources. Rural microfinance initiatives through self-help groups (SHGs) have empowered women, boosting their self-esteem and participation in local governance.
Encouraging female entrepreneurship through schemes like Start-up and Stand-Up India, where a significant number of loans are sanctioned to women, further demonstrates the government's commitment to women-led development, the survey said.
- 22 July 2024 3:41 PM IST
India's spending on R&D less compared to China, US
India is making rapid progress in R&D but the country's investment on it as a percentage of GDP is very low compared to countries like China, the US, and Israel, according to the Economic Survey 2023-24.
Private sector's contribution to R&D also remains low, the survey said.
The link between higher education, industry and research must be strengthened to better translate GERD (gross expenditure on R&D) to research output, according to the document tabled in Parliament on Monday.
It also pointed out that institutions in India develop technologies, but their transformation rate from the lab to the society for the benefit of the people remains low.
"India is making rapid progress in R&D, with nearly one lakh patents granted in FY24, compared to less than 25,000 patent grants in FY20," the survey said.
Citing World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) data, it said India saw the highest growth (31.6 per cent) in patent filings in 2022, demonstrating its evolving innovation landscape and potential for further growth in intellectual property creation.
India has consistently improved its rank in the Global Innovation Index (GII) from 81st position in 2015 to 40th in 2023, as per GII (2023), the survey added.
Further, it said as a mark of India's ascent in high-quality research, the country climbed up to the 9th rank in the Nature's Index 2023, overtaking Australia and Switzerland.
Yet, the survey said, "India's R&D investment as a percentage of GDP stands at 0.64 per cent, compared to China (2.41 per cent), the US (3.47 per cent), and Israel (5.71 per cent)." Moreover, it said, "The private sector's contribution to R&D remains low at 36.4 per cent of the country's GERD compared to China (77 per cent), US (75 per cent)." It, however, noted that GERD in India has been consistently increasing over the years and has more than doubled from Rs 60,196.8 crore in FY11 to Rs 127,381 crore in FY21.
To better translate GERD to research output, the survey said, "The link between higher education, industry and research must be strengthened." "Another challenge is low 'Land to Lab' time. Institutions in India develop technologies, but their transformation rate from the lab to the society for the benefit of the people remains low," it added.
The survey acknowledged that India's share of high-quality research articles, measured in terms of absolute numbers and not percentages, increased 44 per cent in the past four years. However, the country's share remains significantly lower compared to over 20,000 of China and the US each.
On the human resource side, total PhD enrolments in India have increased to 81.2 per cent in FY22 (2.13 lakh) from FY15 (1.17 lakh), the survey noted.
- 22 July 2024 3:39 PM IST
Caution against rise in retail investors in stock market
The Economic Survey on Monday cautioned against significant increase in retail participation in the stock market, saying expectation of higher returns without real market conditions is a matter of concern.
At the same time, it also mentioned that enhanced participation of retail investors lends stability to the capital market and noted the increasing interest of these investors in the derivative trading.
Over the last few years, the Indian capital markets have seen a surge in retail activity through direct trading in markets through their accounts and indirect trading through mutual fund channels.
According to Economic Survey 2023-24, retail investors' share in the equity cash segment turnover was at 35.9 per cent in 2023-24 (FY24). The number of demat accounts with both depositories rose to 1,514 lakh in FY24 from 1,145 lakh in FY23.
The impact of this influx of the investors in the market is also reflected in new investor registrations with the exchanges, their share in total traded value, net investments, and ownership in the listed companies.
For instance, the registered investor base at NSE has nearly tripled from March 2020 to to 9.2 crore as of March 31, 2024, potentially translating into 20 per cent of the Indian households now channelling their household savings into financial markets.
"The significant increase in retail investors in the stock market calls for careful consideration. This is crucial because the possibility of overconfidence leading to speculation and the expectation of even greater returns, which might not align with the real market conditions, is a serious concern," said the document tabled by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in Parliament.
The survey noted that a rise in retail participation was more substantial and steadier through the indirect channel --mutual funds. The FY24 has been a spectacular year for mutual funds as their assets under management (AUM) increased by Rs 14 lakh crore or 35 per cent year-on-year to Rs 53.4 lakh crore at the end of FY24, boosted by mark-to-market (MTM) gains and expansion of the industry.
The total number of folios increased to 17.8 crore at the end of FY24 from 14.6 crore at FY23-end.
Some of the factors that facilitated the entry of investors included seamless technological integration, government measures towards financial inclusion, growth of digital infrastructure, rapid smartphone penetration, a rise of low-cost brokerages, the pursuit of generating income from alternative sources and lower returns generated by traditional asset classes such as real estate and gold.
However, retail investors have cashed in their gains in financial markets and been investing in real assets.
The survey said that the enhanced participation of retail investors in the Indian capital market is hugely welcome and lends stability to the capital market. Also, it has enabled retail investors to earn higher returns on their savings.
Noting the interest of retail investors in the derivative market, the survey said," the derivatives are hedging instruments, they are mostly used as speculative instruments by investors worldwide. India is likely no exception".
"Derivatives trading holds the potential for outsized gains. Thus, it caters to humans' gambling instincts and can augment income if profitable. These considerations are likely driving active retail participation in derivatives trading," the Survey said.
The survey calls for raising investor awareness and continuous financial education to warn them of the low or negative expected returns from derivatives trading.
It, further, said that a significant stock correction could see losses that are more considerable for retail investors participating in capital markets through derivatives.
"Investors’ behavioural response would be to feel 'cheated' by unseen more considerable forces. They may not return to capital markets for a long time. That is a loss to them and the economy," it added.
- 22 July 2024 3:37 PM IST
Case for seeking more FDI from China
Amidst strained ties with China, the pre-budget Economic Survey on Monday made a strong case for seeking foreign direct investments (FDI) from Beijing to boost local manufacturing and tap the export market.
As the US and Europe are shifting their immediate sourcing away from China, it is more effective to have Chinese companies invest in India and then export the products to these markets rather than importing from the neighbouring country, the Survey said.
India faces two choices to benefit from 'China plus one strategy' - it can integrate into China's supply chain or promote FDI from China.
"Among these choices, focusing on FDI from China seems more promising for boosting India's exports to the US, similar to how East Asian economies did in the past.
"Moreover, choosing FDI as a strategy to benefit from the China plus one approach appears more advantageous than relying on trade. This is because China is India's top import partner, and the trade deficit with China has been growing," it added.
It also said that increased foreign direct investment inflows from China can help increase India’s global supply chain participation and push exports.
The Survey explained how increased FDI inflows from China can help in increasing India’s global supply chain participation along with a push to exports.
These economies have typically pursued two main strategies - reducing trade costs and facilitating foreign investment.
At present, the bulk of the FDI coming into India falls under the automatic approval route, however, FDI from countries sharing land borders with India needs mandatory government approval in any sector.
China stands at 22nd position with only 0.37 per cent share (USD 2.5 billion) in total FDI equity inflow reported in India from April 2000 to March 2024.
Countries which share land borders with India are China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar, and Afghanistan.
The Indian and Chinese militaries have been locked in a stand-off since May 2020 and a full resolution of the border row has not yet been achieved though the two sides have disengaged from a number of friction points.
The ties between the two countries nosedived significantly following the fierce clash in the Galwan Valley in June 2020 that marked the most serious military conflict between the two sides in decades.
India has been maintaining that its ties with China cannot be normal unless there is peace in the border areas.
Following these tensions, India has banned over 200 Chinese mobile apps such as Tiktok, Wechat, and Alibaba's UC browser. The country has also rejected a major investment proposal from EV maker BYD.
However, earlier this year the Competition Commission of India (CCI) cleared JSW Group's proposed acquisition of a 38 per cent stake in MG Motor India Pvt Ltd.
MG Motor India is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Shanghai-headquartered SAIC Motor.
The government is also looking at further streamlining processes for timely approval of visas for Chinese professionals and technicians whose expertise is required by the Indian industry to set up manufacturing capacity.
Certain Indian industry players have approached the government stating that they are facing problems in getting visas for Chinese professionals whose expertise is required for things like setting up machines in factories.
Though India has received minimal FDI from China, the bilateral trade between the two nations has grown multi-fold.
China has emerged as the largest trading partner of India with USD 118.4 billion two-way commerce in 2023-24, edging past the US. India's exports to China rose by 8.7 per cent to USD 16.67 billion in the last fiscal.
The main sectors which recorded healthy growth in exports to that country include iron ore, cotton yarn/fabrics/madeups, handloom, spices, fruits and vegetables, plastic and linoleum.
Imports from the neighbouring country increased by 3.24 per cent to USD 101.7 billion. The trade deficit has widened to USD 85 billion in the last fiscal from USD 83.2 billion in 2022-23.
According to the Commerce Ministry data, China was India's top trading partner from 2013-14 till 2017-18 and also in 2020-21. Before China, the UAE was the country's largest trading partner. The US was the largest partner in 2021-22 and 2022-23.
- 22 July 2024 3:35 PM IST
14% of iPhones made in India in FY24
US smartphone major Apple assembled 14 per cent of global iPhones in India in FY24 and the country's ranking in global electronics export improved by four positions, Economic Survey 2023-24 said on Monday.
The Survey, tabled in Parliament by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharamn, said that the mobile phone segment within the electronics sector has experienced the maximum growth with exports to the US rising from USD 2.2 billion in the financial year 2022-23 to USD 5.7 billion in FY24.
"Apple assembled USD 14 billion worth of iPhones in India during FY'24, constituting 14 per cent of its global iPhone production," the Economic Survey said citing third-party data.
Foxconn has started production of Apple mobile phones in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, it added.
"India's share in world electronics exports has improved from 0.63 per cent in 2018 to 0.88 per cent in 2022. As such, India's exports (ranking) rose from 28th in 2018 to 24th in 2022 in global electronics exports. The share of electronics goods in merchandise exports of India rose from 2.7 per cent in FY'19 to 6.7 per cent in FY'24," the survey said.
The survey recorded that India's electronics manufacturing sector has experienced significant growth since 2014, accounting for an estimated 3.7 per cent of the global market share in FY22.
At the same time, the industry contributed 4 per cent to India's total GDP in FY22.
"Domestic production of electronic items increased significantly to Rs 8.22 lakh crore, while exports rose to Rs 1.9 lakh crore in FY'23. India has become an attractive destination for investments in this sector, and substantial manufacturing capacities have been established in the country over the past five years," the survey said.
The economic survey sees smartphone manufacturing as one of the key sector when it comes to riding on geopolitical sentiments among global companies around "China plus one" strategy.
"In the electronics sector, there is a focus on smartphone manufacturing and assembly. The government's PLI scheme, including tax breaks and subsidies, plays a significant role in attracting companies. The rise in India's domestic smartphone demand is also a key factor in companies' decisions to invest there," the report said.
The survey said that while India may not be an immediate beneficiary of the trade diversion from China, it has witnessed a substantial increase in its electronic exports over time due to the roll-out of the PLI scheme.
"The implementation of the PLI scheme has been a key driver of this growth. For instance, India's electronic exports to the US have transitioned from a trade deficit of USD 0.6 billion in FY17 to a trade surplus of USD 8.7 billion in FY'24, underscoring a significant increase in value addition," the report said.
The survey cited a study by Centre for Development Studies which shows that there has been a significant increase in domestic value addition (DVA), employment, wages and salaries in the mobile manufacturing segment since FY17.
"The share of DVA in mobile phone output rose from an average of 8.7 per cent in FY'17 to FY'19 (Phase 1) to 22 per cent in FY'20 to FY'22 (Phase 2), indicating considerable increase in local participation," the survey said.
It said that while the DVA as a ratio of exports may be low, participating in global value chains (GVC) increases in overall value added because of economies of scale in manufacturing for the vast global market.
"The direct workforce in the production of mobile phones has more than tripled between FY'17 to FY'22, particularly benefiting female blue-collar workers. Wages and salaries increased by 317 per cent between phase 1 and phase 2," the survey said.
- 22 July 2024 3:34 PM IST
GST's role in reducing logistics cost
The GST has played a remarkable role in bringing down the country's logistics cost, Economic Survey on Monday said.
The One Nation, One Tax regime has ensured that trucks do not have to wait for hours on state borders, which has brought down the travel time by up to 30 per cent.
“This has reduced the logistics cost and increased the average distance trucks travel from 225 km before GST to 300-325 km,” the Economic Survey 2023-24 tabled in Parliament said.
This has been a great value, adding to the ease of doing business and the growth of manufacturing in the country, it added.
The National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) study of December last year has shown that the logistics cost in the economy has declined 0.8 to 0.9 percentage points of GDP between FY14 and FY22.
India's position in the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index (LPI) rose from 44th place in 2018 to 38th in 2023 out of 139 countries. This improvement is attributed to reduced logistics costs and better trade facilitation.
With the introduction of cargo tracking, dwell time in the eastern port of Visakhapatnam came down from 32.4 days in 2015 to 5.3 days in 2019. Additionally, the country's position in international shipments climbed to 22 in 2023 from 44 in 2018 due to its modernisation and digitalisation efforts.
India moved up five places in infrastructure score and four places up to 48 in logistics competence and equality.
India aims to be in the top 25 countries on the LPI by 2030.