ISRO successfully launches SSLV-D2 to inject three satellites into orbit

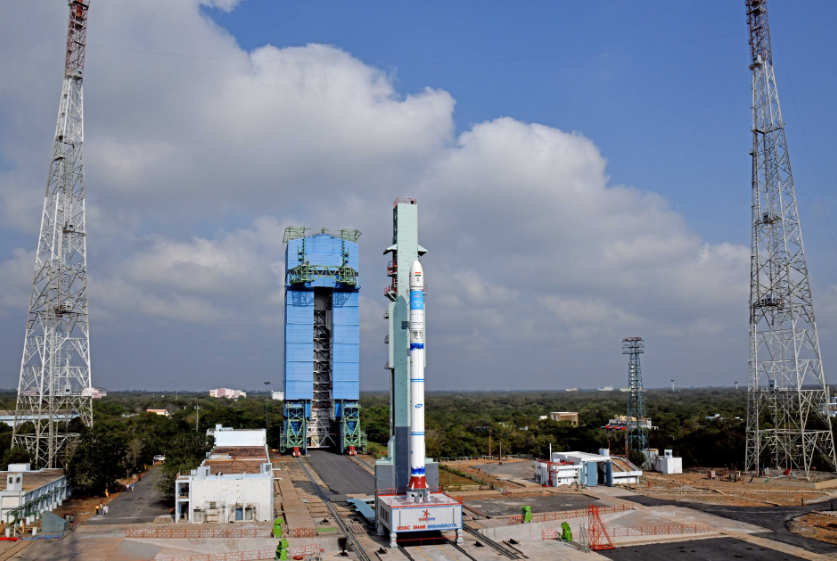
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Friday (February 10) morning launched the second edition of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV-D2) from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
The rocket took off into the skies from the launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre with three satellites – ISRO’s EOS-07, the start-up SpaceKidz’s AzaadiSAT-2 (developed by 750 girl students from India), and the US-based firm Antaris’ Janus-1 at 9:18 am.
#WATCH | Andhra Pradesh: ISRO launches Small Satellite Launch Vehicle-SSLV-D2- from Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota to put three satellites EOS-07, Janus-1 & AzaadiSAT-2 satellites into a 450 km circular orbit pic.twitter.com/kab5kequYF
— ANI (@ANI) February 10, 2023
The Chairman of ISRO, S Somanath, congratulated the three satellite teams for making the satellites and for placing them in the right orbit.
Congratulations to all 3 satellite teams for making the satellites as well as placing them in right orbit. We analysed the problems faced in SSLV-D1, identified corrective actions &implemented them at a very fast pace to ensure the vehicle becomes successful this time: ISRO chief pic.twitter.com/LXJ7LVmyrr
— ANI (@ANI) February 10, 2023
The SSLV is a small-lift launch vehicle developed by ISRO to deliver up to 500 kg satellites to low earth orbit, and has the capability to support multiple orbital drop-offs.
The take-off marked ISRO’s foray into the small satellite launch sector
With the earlier SSLV not living up to the expectations, corrective measures were put in its successor.
A visibly relieved S Somanath said SSLV in its second flight put the three satellites in the intended orbit with precision.
“Congratulations to the space community of India…we have a new launch vehicle, the small satellite SSLV. In its second attempt, SSLV D2 has placed the satellites in the intended orbit precisely. Congrats to all three satellite teams,” he said from the Mission Control Centre (MCC) soon after the successful launch that brought all round smiles.
All the problems related to the previous SSLV launch have been identified, corrective action taken and implemented in good time, Somanath added.
Mission director S Vinod said the ISRO team made a “comeback” in short time soon after the August 7, 2022 failure.
ISRO now has a “new launch vehicle” on offer for the launch vehicle community, he added.
Earlier, the 34-metre tall SSLV soared into majestically into clear skies at 9.18 AM, after a six and a half hour countdown, carrying with it the EOS-07, besides Janus-1 and AzaadiSAT-2 satellites. The rocket placed the satellites into the intended 450-km circular orbit after a 15-odd minute flight. EOS-07 is a 156.3 kg satellite which has been designed, developed and realised by ISRO. New experiments include mm-Wave Humidity Sounder and Spectrum Monitoring Payload. Janus-1, a 10.2 kg satellite, built by Antaris, USA is a technology demonstrator, smart satellite mission, ISRO said.
AzaadiSAT-2, weighing about 8.2 kg is a combined effort of about 750 girl students across India guided by Space Kidz India, Chennai. It aims to demonstrate amateur radio communication capabilities, measure radiation, among others, the space agency added.
According to ISRO, SSLV is capable of launching mini, micro or nano satellites in the 10-500 kg segment into the 500 km planar orbit. It caters to the launch of satellites to Low Earth Orbits (LEO) on “launch-on-demand” basis. It provides low-cost access to Space, offers low turn-around time and flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites, and demands minimal launch infrastructure, ISRO added. It is configured with three solid propulsion stages and a velocity terminal module.
(With inputs from agencies)