Almost one in four Delhiites exposed to coronavirus, reveals study
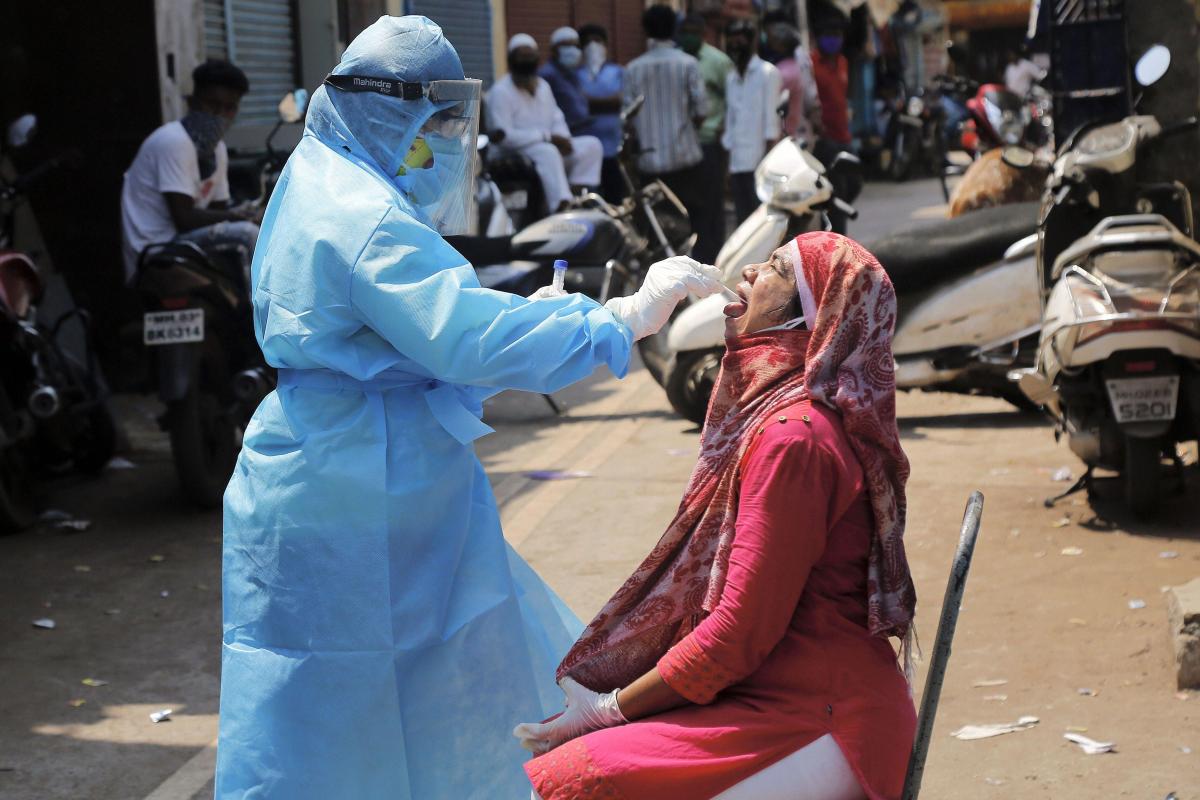
A study commissioned by the Union Health Ministry has revealed that more than 23 per cent of Delhi's population had been exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in the past six months.

A study commissioned by the Union Health Ministry has revealed that more than 23 per cent of Delhi’s population had been exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in the past six months. However, the study also indicated that a large number of infected persons had remained asymptomatic.
The Delhi government and the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) conducted the sero-surveillance study, collecting samples from as many as 21,387 people in the national capital, which has a population of around 2 crore. As per the results, about 47 lakh people had been exposed to the virus.
The study revealed that IgG [Immunoglobulin G] antibodies were present in 23.48 per cent of the total number of people from whom the blood samples were collected. The study was conducted after a careful multi-stage sampling study design from June 27 to July 10. So, experts feel that the number could have increased in the next 10 days.
“Nearly six months into the epidemic, only 23.48 per cent of the people are affected in Delhi, which has several pockets of dense population,” Union Health Ministry said.

“This can be attributed to the proactive efforts taken by the government to prevent the spread of infection including prompt lockdown, effective containment and surveillance measures, including contact tracing and tracking, as well as citizen’s compliance to COVID Appropriate Behaviours,” it added.
“However, a significant proportion of the population is still vulnerable. Therefore, the containment measures need to continue with the same rigour. Non-pharmacological interventions such as physical distancing, use of face mask/cover, hand hygiene, cough etiquette and avoidance of crowded places etc., must be followed strictly,” it said.