
Researchers in India and US develop algorithm for lensless, miniature cameras
Lensless cameras do not have a lens which, in a conventional camera, acts as a focusing element allowing the sensor to capture a sharp photograph of the scene

Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras and Rice University, Texas, have developed
algorithms for lensless, miniature cameras. Such lensless cameras have numerous applications in
areas such as augmented reality, virtual reality, security, smart wearables and robotics where cost, form-factor, and weight are major constraints.
Lensless cameras do not have a lens which, in a conventional camera, acts as a focusing element allowing the sensor to capture a sharp photograph of the scene. Due to the absence of this focusing element, the lensless camera captures a multiplexed or globally blurred measurement of the scene. IIT Madras and Rice University researchers have developed a deep learning algorithm for producing photo-realistic images from the blurred lensless capture.
Taking out a lens can lead to the miniaturisation of a camera. Researchers globally are trying to find substitutes for lenses, IIT Madras said in a statement.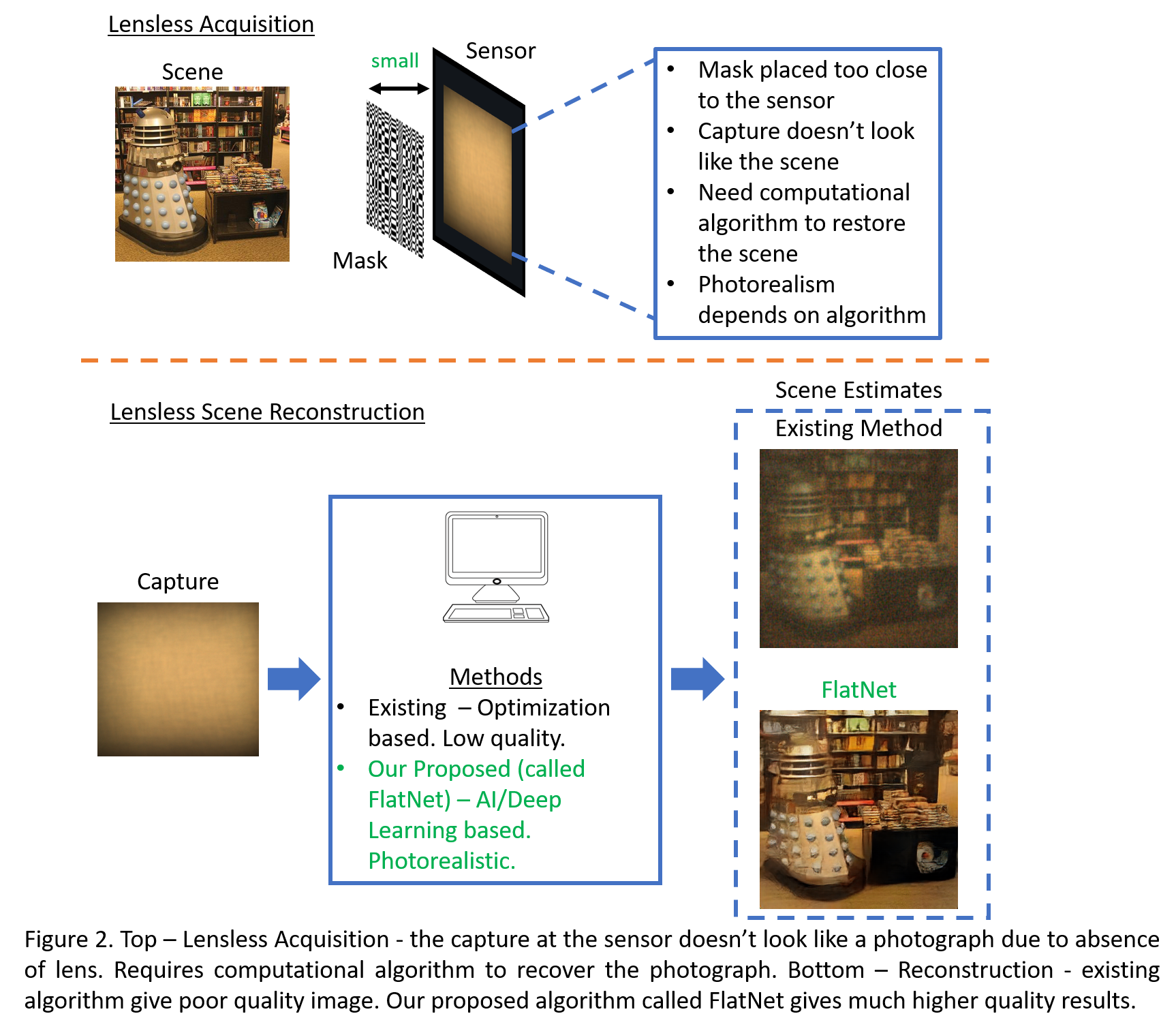
In 2016, Professor Ashok Veeraraghavan’s lab at Rice University registered success in making a lensless camera. They were able to develop a low-cost and low-weight ultra-thin lensless camera. The function of lenses is to focus the incoming light. In these newly developed lensless cameras, a thin optical mask was placed just in front of the sensor at a distance of approximately 1 mm. However, because of the absence of focusing elements, the lensless camera captures blurred images restricting their commercial use.
Researchers have now developed a computational solution to this problem. The team developed a de-blurring algorithm, which can correct the blurred images taken from a lensless camera. The findings were presented as a paper in the prestigious IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and an extended version appeared in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.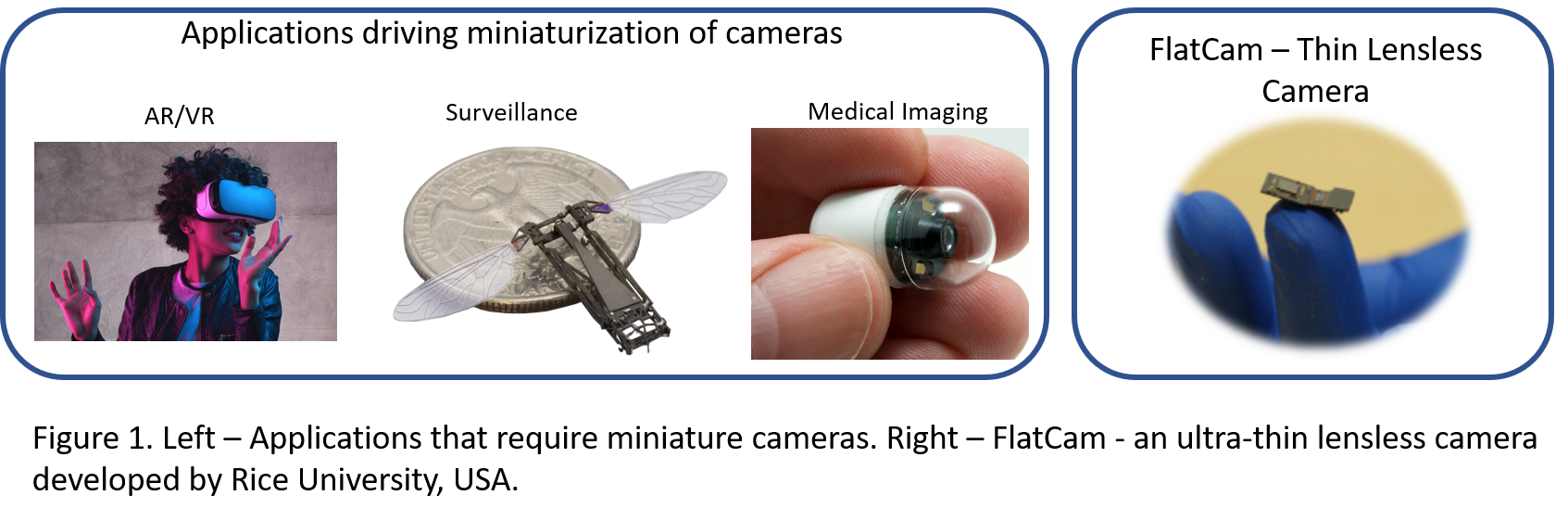
The research was led at IIT Madras by Dr Kaushik Mitra, assistant professor, Department of Electrical Engineering. The team included Salman Siddique Khan, Varun Sundar and Adarsh VR from IIT Madras. Prof Veeraghavan led the Rice University team, which included Dr Vivek Boominathan and Jasper Tan.
“Existing algorithms to de-blur images based on traditional optimisation schemes yield low-resolution ‘noisy images’. Our research team used Deep Learning to develop a reconstruction algorithm called ‘FlatNet’ for lensless cameras, which resulted in significant improvement over traditional optimisation-based algorithms. FlatNet was tested on various real and challenging scenarios and was found to be effective in de-blurring images captured by the lensless camera,” Dr Mitra said.
Also read: Heat to take ‘wind’ out of coastal India; huge job loss anticipated
“Lensless imaging is a new technology and its true potential in solving imaging/vision problems has not been exploited completely. Therefore, we are working on designing newer and better lensless cameras using data-driven techniques, devising efficient algorithms for doing
inference on lensless captures and looking into interesting and important applications like endoscopy and smart surveillance, among other areas, where one can fully realise the benefits of lensless imaging.”
– India Science Wire

