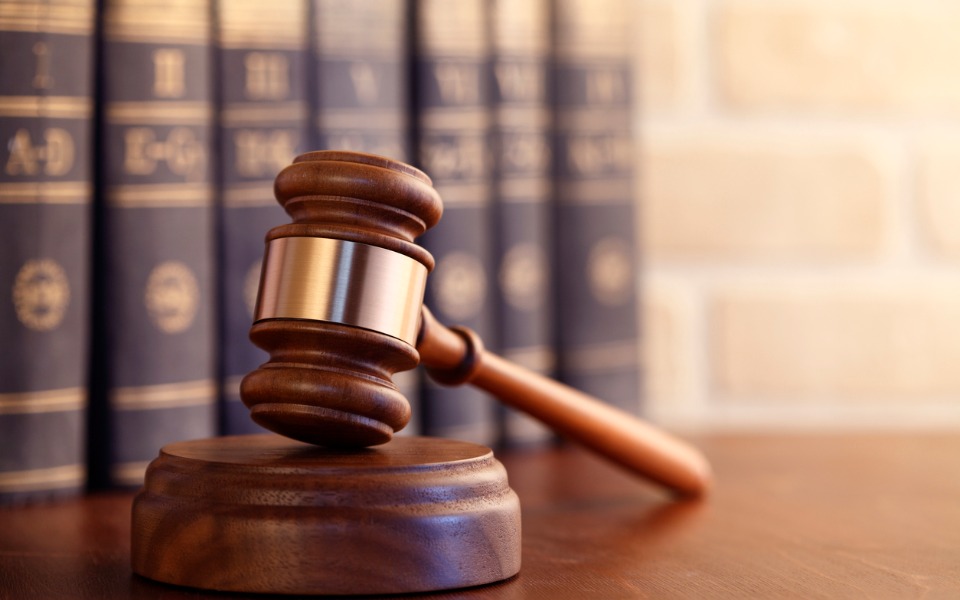
With Sedition Act on hold, some other archaic laws that need a re-look
Since Independence, multiple committees have recommended repeal of such laws; the Law Commission came up with recommendations for repealing obsolete laws in 1957, 1984, 1993, and 2014

With the Supreme Court directing the Centre and states to put on hold all pending trials, appeals, and proceedings with respect to the charges framed under Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), which deals with the offence of sedition, the spotlight has again turned on the laws dating back to the colonial era.
There are many archaic laws which are obsolete and make the legal process long and expensive. Since Independence, multiple committees have recommended the repeal of such laws. The Law Commission came up with recommendations for repealing archaic laws in 1957, 1984, 1993, and the latest one in 2014.
In 1998, a committee under the chairmanship of PC Jain suggested the repeal of over 1,300 such central laws. In 2014, a two-member committee set up by the Prime Minister’s Office listed 1,741 Central Acts for repeal out of 2,781 existing Acts as of October 15 2014, a BBC report said.
Repeal of obsolete laws was also a part of BJP’s 2014 election manifesto. According to PIB in January 2021, “successive governments could remove just 1,301 obsolete laws which came in the way of smooth administration in 66 years whereas the present central government has managed to weed out as many as 1,500 laws in six years”.
Nonetheless, there are still several laws that need to be repealed as they have become irrelevant today. As per the BBC report, these include the Sonthal Parganas Act, 1855; the Indian Treasure Trove Act, 1878; the Government Buildings Act, 1899; and, the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897.
About tribe, treasure, buildings and disease
The Sonthal Parganas Act, 1855, removed the operation of general laws and regulations in certain districts where the Sonthal tribe lives. The act came into force after the Sonthal rebellion against the British authority and the Zamindari system. The Preamble of the Act refers to Sonthals as an ‘uncivilized race of people’ to justify its formulation.
The Indian Treasure Trove Act, 1878, defines ‘treasure’ specifically as “anything of any value hidden in the soil” and worth as little as ₹10. According to the law, the finder of any such treasure needs to inform the Collector of the “nature and amount or approximate value of such treasure and the place where it was found.” The punishment involved is imprisonment for a year and/or a penalty.
Also read: Law Minister cannot draw Lakshman Rekha: Chidambaram on sedition row
The Government Buildings Act, 1899, exempts the buildings and lands owned or in possession of the government in municipality limits from adhering to the municipal building laws. However, with the exception of buildings connected with defence or confidential/secret buildings of the government, a notice of the proposed work should be submitted to the municipal authority before starting work. Though the PC Jain Commission recommended the repeal of the act by state governments, the Law Commission report has suggested modifications for re-enacting the act in the current socio-economic context.
Also read: SC sedition order must be viewed in context of govts positive suggestions: BJP
The Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897, was enacted by the British to deal with the plague that had significantly affected the erstwhile Bombay. The central government is conferred with the power to take measures in the case of an outbreak of epidemic diseases such as inspection of ships or vessels entering or leaving Indian ports. Disobeying the law results in imprisonment for one month and a fine of up to ₹200.
The Act was recently invoked in 2020 during the COVID-19 outbreak which exposed the lacunae in the legislation as there is no mention about the magnitude or severity of the disease, possible spread, international travel and dissemination of vaccines or drugs among other things.